According to the history of Vietnamese alcohol distilleries, Chinese yeast, also known as Chinese medicine yeast, is the oldest and most widely used liquor yeast in the country. It is the core that gives rise to the idea of traditional wine, or traditional Vietnamese wine with a taste that is distinctly reminiscent of traditional Chinese medicine.
The yeast cake's distinctive difference is the presence of Chinese herbs. Traditionally known as Chinese medical yeast, or Chinese yeast, a significant portion also implicitly understands that this is a traditional wine yeast originating from the Northern provinces. (It's possible that the traditional wine yeast originated in the North, which continues to be the region in the nation where it is cooked and distilled the most today.)
Chinese yeast shape:
The yeast is shaped like a round sponge, is the size of a chicken egg, is milky white in color, and has a wrinkled surface. Some people brew their tea with rice hulls for ventilation or as a result of long-standing customs.
Chinese traditional remedies and specific microorganism strains are what give Chinese yeast its distinctive flavor and taste.
Chinese yeast's microbiological composition
Each yeast cake contains three groups: mold, yeast, and bacteria.
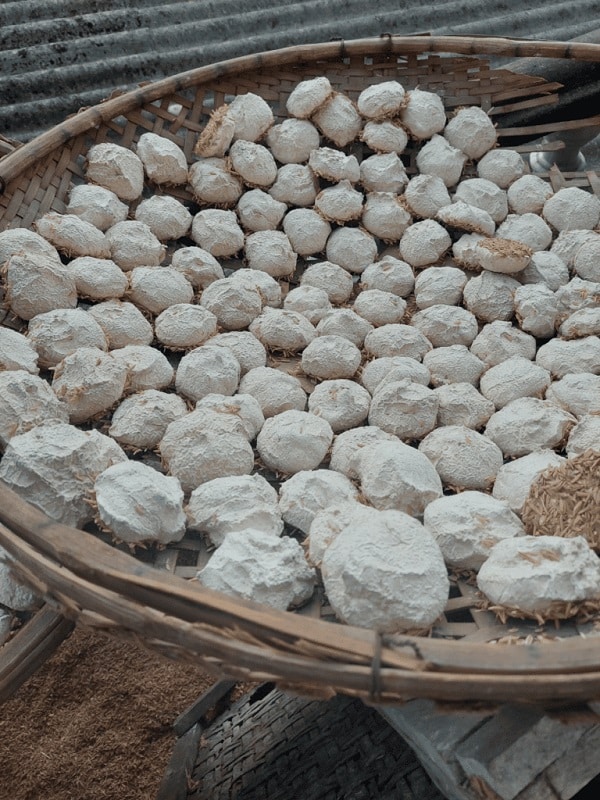

Chinese yeast cake's mold structure
The saccharification process in yeast cake is carried out by the mold. They convert starch to sugar during the fermentation process. On the Mid-year Festival, we eat fermented sticky rice wine, the transformation of these molds produces the sweet flavor.
Although it is accurate to state that mold converts starch to sugar, the following form is preferred: the enzymes that the mold produces turn the starch into sugar. Therefore, companies that make industrial wine and beer do not require mold; instead, they always take the enzyme and add it to starch for saccharification (And where is the enzyme, a business that specializes in growing molds to extract enzymes is there.)
Aspergillus Oryzae (A. oryzae): This mold contains both intracellular and extracellular hydrolytic enzymes in abundance. When the mold's spores are old, they are yellow-green (yellow areca flowers), As a result, we frequently see yellow mold growing on the yeast cake's surface. This mold is very common in nature, showing up everywhere including in food storage facilities, sewers, and furniture. It is particularly prevalent in yeast bread. There are 4 common species:
- Awamorii,
- Usami,
- Niger
- Flavus …

Mucor varieties: These are the mold varieties with milky white, ivory white, because the mold fiber is long but thin, it can surround the yeast cake with a thin membrane. Mucor rouxii, which produces the most alcohol, is the representative.
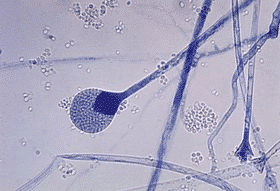
Rhizopus species: This variety produces spores quickly, the spores are a deep black color. The yeast cake's surface consequently appears to have black spots. This species, which prefers varied temperatures (20 to 35 degrees Celsius), is quite active and best in the summer.
Penicillium Species: This mold (green mold) produces green spores. The performance of saccharification is quite good. However, it tastes strongly of mold.
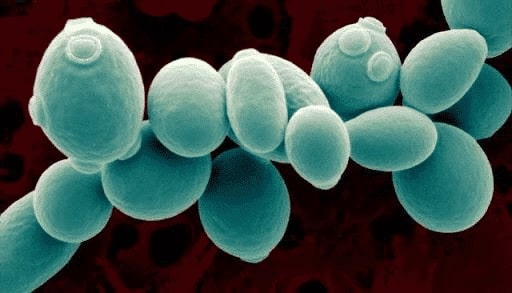
System of yeast in herbal medicine
The yeast system will "eat" the sugar to convert into alcohol (C2H5OH) when given sugar as food.
Although there are many different types of yeast used to make wine and beer, the Saccharomyces line is the most common and well-known strain. There are numerous small strains on this line, but they all produce a lot of alcohol. The Hyphopichia, Burtonii, and Candida strains are wild yeast strains, mixed yeasts.
Common yeasts thrive in environments below 13 degrees of alcohol and grow well at 25 to 28 degrees. However, Saccharomyces species can endure harsher conditions, including temperatures of 32–34 degrees and alcohol concentrations of up to 18.
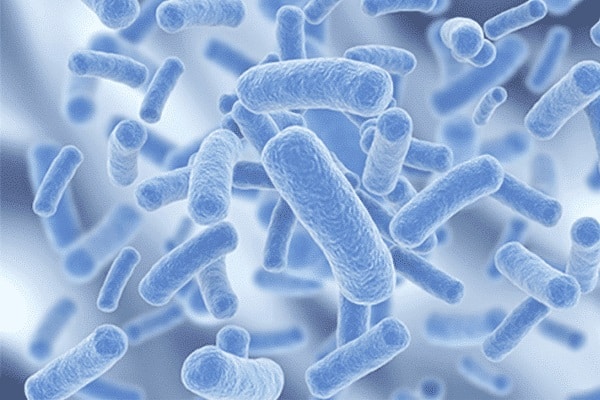
The bacteria in yeast cake:
Mostly unprofitable for wine production:
- Bacteria like lactic acid-producing bacteria and acetic bacteria are frequently found. They are all essentially falsified bacteria, in general.
Sarcina ventriculi bacteria: EMP, pyruvate decarboxylase Glucose + 2ADP +2Pvc => 2 Ethanol +2CO2 + 2ATP
Zymomonas mobilis bacteria: Glucose + ADP + Pvc => 2 Ethanol + 2CO2 + ATP
- Lactic acid bacteria (found in the intestinal tract)
Bacterial groups are undesirable strains and species of microorganisms, but Northern yeast and conventional yeast cake production techniques cannot get rid of them. However, only limiting it in accordance with each yeast maker's unique production secret and the region.
They frequently serve sour, poor, or odd-tasting wine.
=> In a brief overview of microbial structure, Chinese yeast is divided into three groups:
- Mold has the ability to convert starch to sugar.
- After that, the yeast converts the sugar to alcohol.
- The final group is bacteria, which has benefits but also tends to give wine a sour, unpleasant taste.
Depending on the producer, these groups are always present in yeast bread. Some producers use very powerful and plentiful molds, some producers use very powerful and plentiful yeasts, and some producers are occasionally contaminated with bacteria.
The structure according to material
Original yeast cake: are the yeast cakes of good quality. The purpose of the original yeast cake is to breed new batches of strong, superior mold strains and species.
Rice flour: is the substrate for mold, yeast, bacteria to attach and grow.
Chinese medicines: people frequently mention 24-36 Chinese herbs, but it is uncommon for manufacturers to have enough of those. However, there are typically 12 to 14 significant flavors, including licorice, cinnamon, anise, cardamom, mint and largehead atractylodes rhizome.
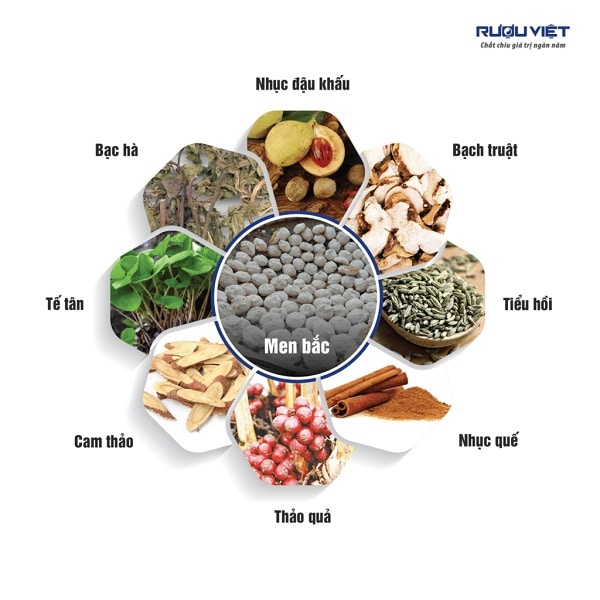

More:: vị men bắc
The characteristics of Chinese yeast
This is the most widely used wine yeast in our country:
- The flavor of wine made with Chinese yeast is very delicious and distinctive: The pungent and delicate flavor, the aroma of Chinese herbs, the aroma of orange peel, and the hazy aroma of wine vinegar. However, there is no sour taste; instead, after drinking, one "feels" a sweet, soothing taste in the throat.
- Low efficiency: only slightly better than leaf yeast. When compared to the probiotic line, 100kg of plain rice is only 70-75l of 40 degree wine.
- Long fermentation time, averaging 13-18 days from yeast to distillation. A winery with a fermentation time of 5 -9 days will almost certainly not use 100% Chinese yeast.
- Chinese medical liquor is expensive due to the long incubation time and low alcohol production efficiency.
The reality about contemporary Chinese yeast
In Vietnam, this enamel line has deteriorated over the last 15 years, losing its number one position. Because of its higher economic efficiency, it is overrun by probiotic strains. Probiotic strains overwhelmed it because they are more cost effective. Also, because of the user's ease and sophistication, the mixing of the makers.
Some traditional Chinese herbs have lost their flavor and active ingredients as a result of growth stimulant cultivation or chemical preservation and herbs in nature are becoming increasingly scarce. Prestigious yeast makers and masters are often very strict in choosing herbs or only importing 1st grade drugs, so the wine will be more delicious than choosing 2nd and 3rd grade components.
Chinese medicinal herbs are not the key secret, as yeast manufacturers have long claimed, but preserving pure strains of microorganisms (micro-yeasts, micro-molds) in traditional Chinese yeast cakes is a difficult and critical problem because those microorganism strains are only degraded after 5-7 or a few dozen times of propagation (used as yeast food). To discover the secret to preserving and developing these strains, it is necessary to conduct extensive microbiology research, apply modern science, combine with continuous trial and error practice, and pay many times (details will be shared in the intensive article).
More: Vodka là gì? Top 5 hãng rượu vodka nổi tiếng nhất thế giới

Hiếm lắm mới đọc được bài viết chuyên sâu như vậy
Pingback: Rượu Men Lá Suối Khuông - Văn Hóa & Tập Tục Người Mường